The majority of businesses work with several partners and third-party vendors in various ways. This might include suppliers, IT providers, marketing agencies, accounting firms and many more.
Depending on the nature of the partnership, you may need to exchange large amounts of data with these businesses, including customer details. However, this can pose a security risk.
Criminals specifically target businesses within supply chains. If they’re successful with a cyber attack, they gain not only the information of that businesses, but other organisations it works with too. This can give them access to vast amount of data, bringing greater gains.
Too often, deliberate cyber attacks (normally involving malware) can easily reach businesses in the chain through several vulnerable access points.
Accenture conducted research into supply chain security, finding that 40% of cyber attacks originate within the extended supply chain rather than within businesses themselves.
It’s important to note that the security of a supply chain is only as strong as the weakest member of the chain. Cyber criminals identify the vulnerabilities of the weakest member to gain access to the other members of the supply chain.
In order to prevent supply chain attacks, every member must strengthen their security posture. In this blog, we examine what you can do to improve yours and prevent supply chain attacks.
How are supply chains attacked?
Supply chain attacks commonly occur from third-party software providers, third-party data storage, websites and watering holes, which are all used to distribute malware. We briefly explore each method below.
Third-party software providers
Attacks occur through malicious malware or counterfeit components embedded into software and stored in repositories that businesses regard as secure. The software is downloaded by users, which then installs both the software and the malicious malware within it.
The compromised software is difficult to detect, so there is little clues for security teams to suspect it’s not legitimate. One significant example of this the Petya Ransomware outbreak, which hit businesses globally and infect millions of computers.
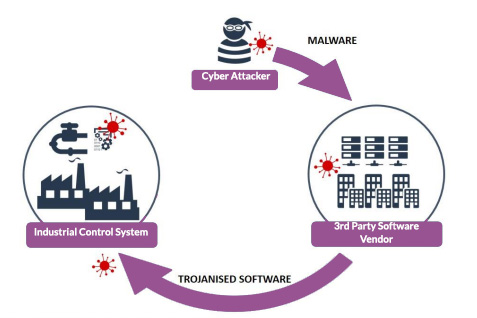
Image from https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
Third-party data storage
Many businesses store their data with third-party companies, which aggregate, store and process the data.
However, some data storage providers are not fully secure and can be targeted by cyber criminals. They then have the potential to cause large scale fraud with other links of the supply chain.
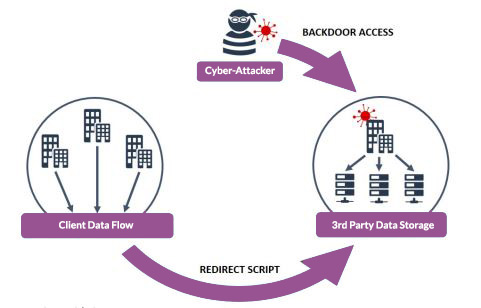
Image from https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
Websites
Cyber criminals can easily access insecure websites and add redirect scripts, sending visitors to a malicious domain where malware is automatically downloaded. This could be the website of one of your third-party providers, which would then infect your business if your staff or clients visit the site.
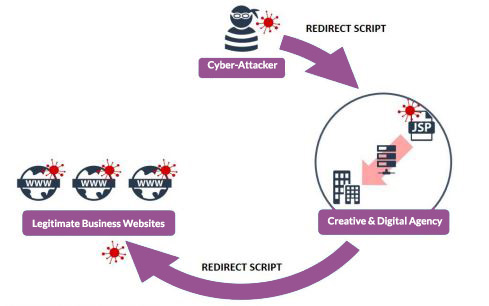
Image from https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
Watering holes
A watering hole supply chain attack is where cyber criminals identify a website with high amounts of traffic. Typically, these include government, finance and healthcare websites.
Once hacked, they use this website as a base to distribute malware. It then infects users’ devices and other related networks.
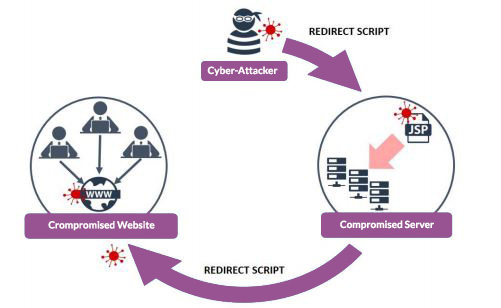
Image from https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
What is the impact of a supply chain attack?
A supply chain attack can have far-reaching consequences for organisations involved. Here are some of the potential impacts:
- Financial losses: An attack can bring direct costs (such as legal fees and system remediation) and indirect costs (loss of revenue due to disruption or reduced trust) to every member of the chain. You may also face fines if the attack leads to a breach, due to non-compliance to the likes of GDPR.
- Reputational damage: Customers, partners and investors may lose confidence if an attack leads to data loss or non-compliance. You may also face negative media coverage which can further damage trust in your business.
- Operational disruption: Individual businesses may face IT outages, data loss and system downtime if an attacker gets hold of their systems. This will reduce productivity, as employees wait for the issues to be rectified. Across the supply chain, you may also face shortages and delays, resulting in further disruption.
- Exposure of sensitive information: Customer data, intellectual property and financial information may be stolen and misused in the event of an attack, which can leave people susceptible to identity theft.
- Legal consequences: In the event of data breaches, affected or organisations may file lawsuits for damages. You’ll also face scrutiny from data protection and cyber security regulators.
Preventing a supply chain attack
The more steps a business takes to improve their own security, the more secure supply chains will become.
Fortunately, there are a few things you can do to improve the security of your business. It’s also worth checking that organisations you work with follow similar principles in their own IT provisions.
- Build security declarations into vendor and supplier agreements: Although these suppliers aren’t employees, you’re sharing important information and data with them . While you may be able to trust your own security set up, can you rely on someone else’s? A data security policy should be part of a supplier agreement to give you security and reassurance.
- Use endpoint protection for devices: Endpoint protection plays a crucial role in mitigating supply chain attack risks by preventing initial infection through malware. It can also contain threats and protect data through encryption and data loss prevention. Every device in your business should be protected. Microsoft Defender is a great tool for this.
- Improve staff awareness: Provide business cyber security training to ensure all employees understand and identify possible threats. Additionally, train all staff not to keep passwords or private data stored in personal folders on their computers, as this makes it easier to steal. Obtaining Cyber Essentials certification is a great way to get your business started.
- Encrypt all devices: Encryption safeguards data by transforming it into an unreadable format that requires a specific decryption key. This process protects sensitive information from unauthorised access, ensuring confidentiality.
- Install patch updates: Ensure automatic updates are turned on across your software solutions. This reduces the risk of running on an unsupported or out of date system that hold vulnerabilities.
- Have back up in place: By regularly creating and storing copies of critical data in secure locations, you can mitigate the impact of data loss caused by a supply chain attack. A disaster recovery and backup strategy outline procedures for restoring systems and data, minimising downtime, financial losses and reputational damage.
Access enhanced security protection against cyber attacks
Infinity Group are IT security specialists and GDPR consultants. Our cyber security experts have worked with countless businesses to strengthen their security posture and protect them against cyber criminals. They have advanced knowledge of modern cyber threats, allowing them to ensure you’re ready for emerging risks.
We can also alleviate the burden of security on your IT team, allowing you to focus on everything else with the peace of mind you’re adequately protected.
Find out more about our cyber security consultancy services.

